Home
- POV-Ray Tutorial
- Geometrical Basics
for Raytracing
Right-angled Triangle
Pythagorean Theorem
Trigonometry Basics
Law of cosines
Equilateral Triangle
Regular Polygon
Polyhedron
Tetrahedron
Octahedron
Cube & Cuboid
Dodecahedron
Icosahedron
Cuboctahedron
Truncated Octahedron
Rhombicuboctahedron
Truncated Icosahedron
Circles
Tangent circles
Internal Tangents
External Tangents
- Geometric 3D Animations
|
| |
Regular Polygon
A regular polygon is a polygon with the properties, that all angles are equal and all sides have the same length.
The equilateral triangle (3), the sqare (4), the regular pentagon (5), the regular hexagon (6), the heptagon (7),
the octagon (8), the nonagon or enneagon (9), the decagon (10), the hendecagon (11), the dodecagon (12), ... ,
the hectagon (100), the chiliagon (1000), the miriagon (10000), the megagon (1000000),
the gigagon (1000 000 000), the teragon (1000 000 000 000 000 000),
the petagon (1000 000 000 000 000 000 000), ... , the circle (∞).
|
Note: The trigonometric functions sin(X), cos(X) and tan(X) in POV-Ray
need their arguments X in radians !!! The symbole π = pi en POV-Ray.
|
In a regolar polygon with N corners or N sides:
The sum of the interior angles = 180*(N-2);
The interior angle = 180-360/N;
equilateral triangle: 180-360/3 = 180 - 120 = 60;
sqare: 180-360/4 = 180 - 90 = 90;
regular pentagon: 180-360/5 = 180 - 72 = 108;
regular hexagon: 180-360/6 = 180 - 60 = 120;
regolar heptagon: 180-360/7 = 180-51,43 = 128,57;
regolar octagon: 180-360/8 = 180 - 45 = 135;
regolar enneagon: 180-360/9 = 180 - 40 = 140;
regolar decagon: 180-360/10= 180 - 36 = 144;
regolar hendecagon: 180-360/11= 180 -32,7 = 147,3;
regolar dodecagon: 180-360/12= 180 - 30 = 150; |
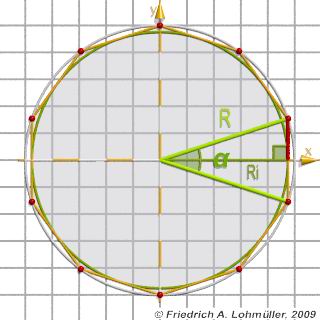
A regolar polygon with N corners and
with the radius of the circumcircle R,
or with the radius of the incircle Ri:
The length of side a:
a = 2* R * sin( radians( 180/N ) ); or
a = 2*R *sin( pi/N );
a = 2* Ri * tan( radians( 180/N ) ); or
a = 2*Ri*tan( pi/N );
|
With the length of the side a of the regolar polygon :
The radius of the circumcircle:
R = 1/2 * a/sin( radians( 180/N ) ) ); o
R = 1/2 * a/sin( pi/N );
The radius of incircle:
Ri = 1/2 * a/tan( radians( 180/N ) ) ); o
Ri = 1/2 * a/tan( pi/N );
|
|
A regolar polygon - angles, sides, radii.
|
|