Home
- POV-Ray Tutorial
- Geometrical Basics
for Raytracing
Right-angled Triangle
Pythagorean Theorem
Trigonometry Basics
Law of cosines
Equilateral Triangle
Regular Polygon
Polyhedron
Tetrahedron
Octahedron
Cube & Cuboid
Dodecahedron
Icosahedron
Cuboctahedron
Truncated Octahedron
Rhombicuboctahedron
Truncated Icosahedron
Circles
Tangent circles
Internal Tangents
External Tangents
- Geometric 3D Animations
|
Equilateral Triangle
In the following we write for the square root of a number the expression "sqrt(ZAHL)"
conforming to the syntax used in POV-Ray.
Note: To avoid any collision with built-in identifiers and reserved words in POV-Ray,
it's strongly recommanded to use only words beginning with capital letters
for all identifiers of variables declared by the user, i.e. use "Ri" instead of "r"
and use "H" instead of "h".
|
|
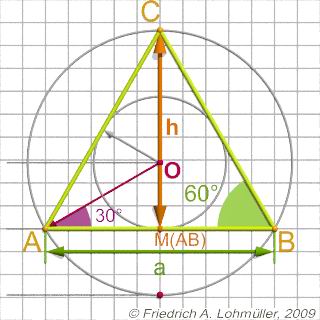
Dimensions
Length of triangle base side: a.
All internal angles: 60° |
The height
of an equilateral triangle:
h = 1/2 * sqrt(3) * a ; or
h = sin (radians(60)) * a ;
The height of the incenter O or
the incircle radius
of an equilateral triangle:
r = 1/6 * sqrt(3) * a ;
The radius of circumcircle
of an equilateral triangle:
R = 1/3 * sqrt(3) * a ;
|
|
An equilateral triangle
|
|