Home
- POV-Ray Tutorial
- Geometrical Basics
for Raytracing
Right-angled Triangle
Pythagorean Theorem
Trigonometry Basics
Law of cosines
Equilateral Triangle
Regular Polygon
Polyhedron
Tetrahedron
Octahedron
Cube & Cuboid
Dodecahedron
Icosahedron
Cuboctahedron
Truncated Octahedron
Rhombicuboctahedron
Truncated Icosahedron
Circles
Tangent circles
Internal Tangents
External Tangents
- Geometric 3D Animations
|
 |
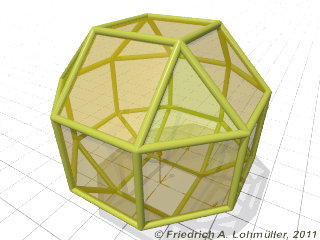
Rhombicuboctahedron
(small Rhombicuboctahedron)
Some useful geometrical facts. |
 Folding of a Rhombicuboctahedron
Folding of a Rhombicuboctahedron |
In the following we write for the square root of a number
the expression "sqrt(ZAHL)"
conforming to the syntax used in POV-Ray.
|
Dimensions
Length of an edge: a. |
The radius of circumsphere:
R = a / 2 * sqrt( 5 + 2*sqrt(2));
The radius of edgesphere (tangent to edges):
Re = a / 2 * sqrt( 4 + 2*sqrt(2) );
Coordinates of the corners:
all permutations of ( +/-1, +/-1, +/-(1+sqrt(2)) );
The angle between square and square: 135°
SS_Angle = degrees(acos(-1/sqrt(2)));
The angle between square and triangle: ~144,74°
ST_Angle = degrees(acos(-sqrt(2/3)));
The angle between edges: 135°
Edge_Angle = degrees(acos(-1/sqrt(2)));
|
|
Rhombicuboctahedron
|
|

 Folding of a Rhombicuboctahedron
Folding of a Rhombicuboctahedron